WebThe process of inhalation occurs due to an increase in the lung volume (diaphragm contraction and chest wall expansion) which results in a decrease in lung pressure in comparison to the atmosphere; thus, air rushes in the airway. The difference in pressures drives pulmonary ventilation because air flows down a pressure gradient, that is, air flows from an area of higher pressure to an area of lower pressure. The neural networks direct muscles that form the walls of the thorax and abdomen and produce pressure gradients that move air into and out of the lungs. The diaphragm is a sheet of muscle that separates Intrapulmonary and Intrapleural Pressure Relationships. The CPAP machine has a mask that covers the nose, or the nose and mouth, and forces air into the airway at regular intervals. flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process info@meds.or.ke Breathing is an active process - requiring the contraction of skeletal muscles. The control of ventilation is a complex interplay of multiple regions in the brain that signal the muscles used in pulmonary ventilation to contract (Table 22.1). 

 2023 Healthline Media UK Ltd, Brighton, UK. In emphysema, the alveolar walls lose their elasticity and are destroyed, often by a build-up of damage and debris being cleaned up by alveolar macrophages (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)). Normal and quiet inspiration is carried out by the diaphragm, which lengthens and shortens the chest cavity. Young, James A. Watch this video to learn more about lung volumes and spirometers. No matter what, the words that usually come out of those around you are breathe, just breathe slowly and relax. But, what is breathing? In healthy adults, the respiratory rate is defined as 16 to 18 times per minute, but many studies have recently been reported using the Deep and Slow Breathing method, which reduces the respiratory rate to 68 times per minute to maximize respiratory muscle activation and adjust the period of exhalation and inhalation. It is a dose-response, negative-feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus, the greater the response. Your bronchial tubes lead to smaller air passages called bronchi, and then into bronchioles. WebThe decrease in volume causes pressure within the lungs that is greater than that of the environment. The apneustic center is a double cluster of neuronal cell bodies that stimulate neurons in the DRG, controlling the depth of inspiration, particularly for deep breathing. Respiratory rate is defined as the number of breaths taken per minute. The nasal cavity also moderates the temperature of the inhaled air. flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process. Between the two layers is the pleural cavity, a potential space containing a very small quantity of fluid, important for lubrication and cohesion of the pleural layers. Air flows out of the lungs during expiration based on the same principle; pressure within the lungs becomes greater than the atmospheric pressure. Anatomy of breathing: want to learn more about it? As you recall, carbon dioxide is a waste product of cellular respiration and can be toxic. Inhalation and exhalation move air into and out of the lungs. So far, you have seen how the thoracic cage is a frame that encloses the respiratory system and allows breathing to take place. The respiratory system is made up of the nose, sinuses, lungs, diaphragm and other organs and structures. By expanding the thoracic cavity and thus the lungs, the increased volume results in a decrease in the lung air pressure. During a breathing cycle, the lungs can be expanded and contracted in two ways. There are 11 pairs of external intercostals, extending between the tubercles of the ribs and the costochondral joints. The breathing cycle is controlled by the respiratory centre located inside the medulla oblongataand the pons of the brain stem. The expansion of the thoracic cavity directly influences the capacity of the lungs to expand. A child under 1 year of age has a normal respiratory rate between 30 and 60 breaths per minute, but by the time a child is about 10 years old, the normal rate is closer to 18 to 30.
2023 Healthline Media UK Ltd, Brighton, UK. In emphysema, the alveolar walls lose their elasticity and are destroyed, often by a build-up of damage and debris being cleaned up by alveolar macrophages (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)). Normal and quiet inspiration is carried out by the diaphragm, which lengthens and shortens the chest cavity. Young, James A. Watch this video to learn more about lung volumes and spirometers. No matter what, the words that usually come out of those around you are breathe, just breathe slowly and relax. But, what is breathing? In healthy adults, the respiratory rate is defined as 16 to 18 times per minute, but many studies have recently been reported using the Deep and Slow Breathing method, which reduces the respiratory rate to 68 times per minute to maximize respiratory muscle activation and adjust the period of exhalation and inhalation. It is a dose-response, negative-feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus, the greater the response. Your bronchial tubes lead to smaller air passages called bronchi, and then into bronchioles. WebThe decrease in volume causes pressure within the lungs that is greater than that of the environment. The apneustic center is a double cluster of neuronal cell bodies that stimulate neurons in the DRG, controlling the depth of inspiration, particularly for deep breathing. Respiratory rate is defined as the number of breaths taken per minute. The nasal cavity also moderates the temperature of the inhaled air. flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process. Between the two layers is the pleural cavity, a potential space containing a very small quantity of fluid, important for lubrication and cohesion of the pleural layers. Air flows out of the lungs during expiration based on the same principle; pressure within the lungs becomes greater than the atmospheric pressure. Anatomy of breathing: want to learn more about it? As you recall, carbon dioxide is a waste product of cellular respiration and can be toxic. Inhalation and exhalation move air into and out of the lungs. So far, you have seen how the thoracic cage is a frame that encloses the respiratory system and allows breathing to take place. The respiratory system is made up of the nose, sinuses, lungs, diaphragm and other organs and structures. By expanding the thoracic cavity and thus the lungs, the increased volume results in a decrease in the lung air pressure. During a breathing cycle, the lungs can be expanded and contracted in two ways. There are 11 pairs of external intercostals, extending between the tubercles of the ribs and the costochondral joints. The breathing cycle is controlled by the respiratory centre located inside the medulla oblongataand the pons of the brain stem. The expansion of the thoracic cavity directly influences the capacity of the lungs to expand. A child under 1 year of age has a normal respiratory rate between 30 and 60 breaths per minute, but by the time a child is about 10 years old, the normal rate is closer to 18 to 30. 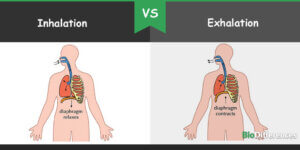
 Ease into the topic and cement your knowledge using Kenhub's respiratory system quizzes and labeled diagrams. By the end of this section, you will be able to: The processes of the respiratory system follow oxygen from its origin in the air you inhale to its use by cells of the body to convert glucose to cellular energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). By lifting the ribs and pushing the abdominal organs down, the intrathoracic volume increases. The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system, as they perform a vital role in breathing: gas exchange.
Ease into the topic and cement your knowledge using Kenhub's respiratory system quizzes and labeled diagrams. By the end of this section, you will be able to: The processes of the respiratory system follow oxygen from its origin in the air you inhale to its use by cells of the body to convert glucose to cellular energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). By lifting the ribs and pushing the abdominal organs down, the intrathoracic volume increases. The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system, as they perform a vital role in breathing: gas exchange. 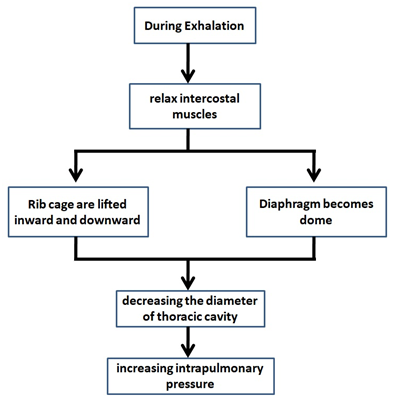 During forced expiration, accessory muscles of the abdomen, including the obliques, contract, forcing abdominal organs upward against the diaphragm. Last medically reviewed on July 29, 2020, The lungs are self-cleaning organs, but people can also use certain methods to clear mucus and open up the airways. A shallow breath, called costal breathing, requires contraction of the intercostal muscles. The major brain centers involved in pulmonary ventilation are the medulla oblongata and the pontine respiratory group (Figure 22.20). Concentration changes in certain substances, such as carbon dioxide or hydrogen ions, stimulate these receptors, which in turn signal the respiration centers of the brain. The hypothalamus and other regions associated with the limbic system are involved in regulating respiration in response to emotions, pain, and temperature. Eventually, in those with severe COPD, even treatment with supplemental oxygen will not be sufficient to prevent respiratory failure. A child under 1 year of age has a normal respiratory rate between 30 and 60 breaths per minute, but by the time a child is about 10 years old, the normal rate is closer to 18 to 30. For example, the tongue and throat muscles of some individuals with obstructive sleep apnea may relax excessively, causing the muscles to push into the airway. This This article examines the various parts of the respiratory system, some respiratory conditions, and how a person breathes. Atmospheric pressure is the amount of force that is exerted by gases in the air surrounding any given surface, such as the body. Explain how spirometry test results can be used to diagnose respiratory diseases or determine the effectiveness of disease treatment. Pneumonia symptoms and diagnosis. In contrast, low levels of carbon dioxide in the blood cause low levels of hydrogen ions in the brain, leading to a decrease in the rate and depth of pulmonary ventilation, producing shallow, slow breathing. vsvarsha7920 vsvarsha7920 21.08.2019 Advertisement Advertisement In addition, accessory muscles (primarily the internal intercostals) help to compress the rib cage, which also reduces the volume of the thoracic cavity. Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory cycle. In some cases, the cause of central sleep apnea is unknown. The pneumotaxic centre located dorsally in the superior portion of the pons controls the rate and depth of breathing. In addition to the contraction of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, other accessory muscles must also contract. Along Mombasa Road. A decrease in volume leads to a(n) ________ pressure. The process of breathing takes place with the lungs of the organism. All of the above skeletal components complete the thoracic cage from anterior to posterior, offering both protection and flexibility for ventilation. Inhalation. Internal respiration is the process of gas exchange between the blood in capillaries at the cells of the tissues of the body. The normal respiratory rate of a child decreases from birth to adolescence. Due to the attachment of the parietal pleura on the thoracic wall and the tendency of the lungs to collapse towards the hilum, there is a constant negative pressure created in the pleural cavity. For example, an increase in body temperature causes an increase in respiratory rate. Step 2 Air rushes in through the nose and mouth and passes through the throat. A small tubular diameter forces air through a smaller space, causing more collisions of air molecules with the walls of the airways. To initiate breathing, the dorsal respiratory group sends impulses through the phrenic nerve towards the diaphragm and through the intercostal nerves towards the external intercostal muscles. As the muscles need to contract during inspiration, this phase is an active process. In the larynx, the airways are reinforced by C-shaped hyaline cartilage rings. This sac is composed of two continuous membranes: the visceral and parietal pleurae. Its most vital function is to enable airflow to and from the lungs. Our mission is to improve educational access and learning for everyone. Other characteristics of the lungs influence the effort that must be expended to ventilate. and grab your free ultimate anatomy study guide! Intrapleural pressure is the pressure of the air within the pleural cavity, between the visceral and parietal pleurae. 2023 Basically, the affected portion of the wall moves inwards on inspiration and outwards on expiration (paradoxical motion), creating pain and impairing ventilation. Since the parietal pleura is attached to the thoracic wall, the natural elasticity of the chest wall opposes the inward pull of the lungs. With so many working parts, keeping the respiratory system healthy is important. These episodes may last for several seconds or several minutes, and may differ in the frequency with which they are experienced. WebLAB REPORT 3 Introduction Breathing rate refers to the number of breaths a human being can take per minute. Likewise, if volume decreases, pressure increases. One way of doing this is to change the anteroposterior diameter of the chest cavity by elevating or depressing the ribs.
During forced expiration, accessory muscles of the abdomen, including the obliques, contract, forcing abdominal organs upward against the diaphragm. Last medically reviewed on July 29, 2020, The lungs are self-cleaning organs, but people can also use certain methods to clear mucus and open up the airways. A shallow breath, called costal breathing, requires contraction of the intercostal muscles. The major brain centers involved in pulmonary ventilation are the medulla oblongata and the pontine respiratory group (Figure 22.20). Concentration changes in certain substances, such as carbon dioxide or hydrogen ions, stimulate these receptors, which in turn signal the respiration centers of the brain. The hypothalamus and other regions associated with the limbic system are involved in regulating respiration in response to emotions, pain, and temperature. Eventually, in those with severe COPD, even treatment with supplemental oxygen will not be sufficient to prevent respiratory failure. A child under 1 year of age has a normal respiratory rate between 30 and 60 breaths per minute, but by the time a child is about 10 years old, the normal rate is closer to 18 to 30. For example, the tongue and throat muscles of some individuals with obstructive sleep apnea may relax excessively, causing the muscles to push into the airway. This This article examines the various parts of the respiratory system, some respiratory conditions, and how a person breathes. Atmospheric pressure is the amount of force that is exerted by gases in the air surrounding any given surface, such as the body. Explain how spirometry test results can be used to diagnose respiratory diseases or determine the effectiveness of disease treatment. Pneumonia symptoms and diagnosis. In contrast, low levels of carbon dioxide in the blood cause low levels of hydrogen ions in the brain, leading to a decrease in the rate and depth of pulmonary ventilation, producing shallow, slow breathing. vsvarsha7920 vsvarsha7920 21.08.2019 Advertisement Advertisement In addition, accessory muscles (primarily the internal intercostals) help to compress the rib cage, which also reduces the volume of the thoracic cavity. Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory cycle. In some cases, the cause of central sleep apnea is unknown. The pneumotaxic centre located dorsally in the superior portion of the pons controls the rate and depth of breathing. In addition to the contraction of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, other accessory muscles must also contract. Along Mombasa Road. A decrease in volume leads to a(n) ________ pressure. The process of breathing takes place with the lungs of the organism. All of the above skeletal components complete the thoracic cage from anterior to posterior, offering both protection and flexibility for ventilation. Inhalation. Internal respiration is the process of gas exchange between the blood in capillaries at the cells of the tissues of the body. The normal respiratory rate of a child decreases from birth to adolescence. Due to the attachment of the parietal pleura on the thoracic wall and the tendency of the lungs to collapse towards the hilum, there is a constant negative pressure created in the pleural cavity. For example, an increase in body temperature causes an increase in respiratory rate. Step 2 Air rushes in through the nose and mouth and passes through the throat. A small tubular diameter forces air through a smaller space, causing more collisions of air molecules with the walls of the airways. To initiate breathing, the dorsal respiratory group sends impulses through the phrenic nerve towards the diaphragm and through the intercostal nerves towards the external intercostal muscles. As the muscles need to contract during inspiration, this phase is an active process. In the larynx, the airways are reinforced by C-shaped hyaline cartilage rings. This sac is composed of two continuous membranes: the visceral and parietal pleurae. Its most vital function is to enable airflow to and from the lungs. Our mission is to improve educational access and learning for everyone. Other characteristics of the lungs influence the effort that must be expended to ventilate. and grab your free ultimate anatomy study guide! Intrapleural pressure is the pressure of the air within the pleural cavity, between the visceral and parietal pleurae. 2023 Basically, the affected portion of the wall moves inwards on inspiration and outwards on expiration (paradoxical motion), creating pain and impairing ventilation. Since the parietal pleura is attached to the thoracic wall, the natural elasticity of the chest wall opposes the inward pull of the lungs. With so many working parts, keeping the respiratory system healthy is important. These episodes may last for several seconds or several minutes, and may differ in the frequency with which they are experienced. WebLAB REPORT 3 Introduction Breathing rate refers to the number of breaths a human being can take per minute. Likewise, if volume decreases, pressure increases. One way of doing this is to change the anteroposterior diameter of the chest cavity by elevating or depressing the ribs. 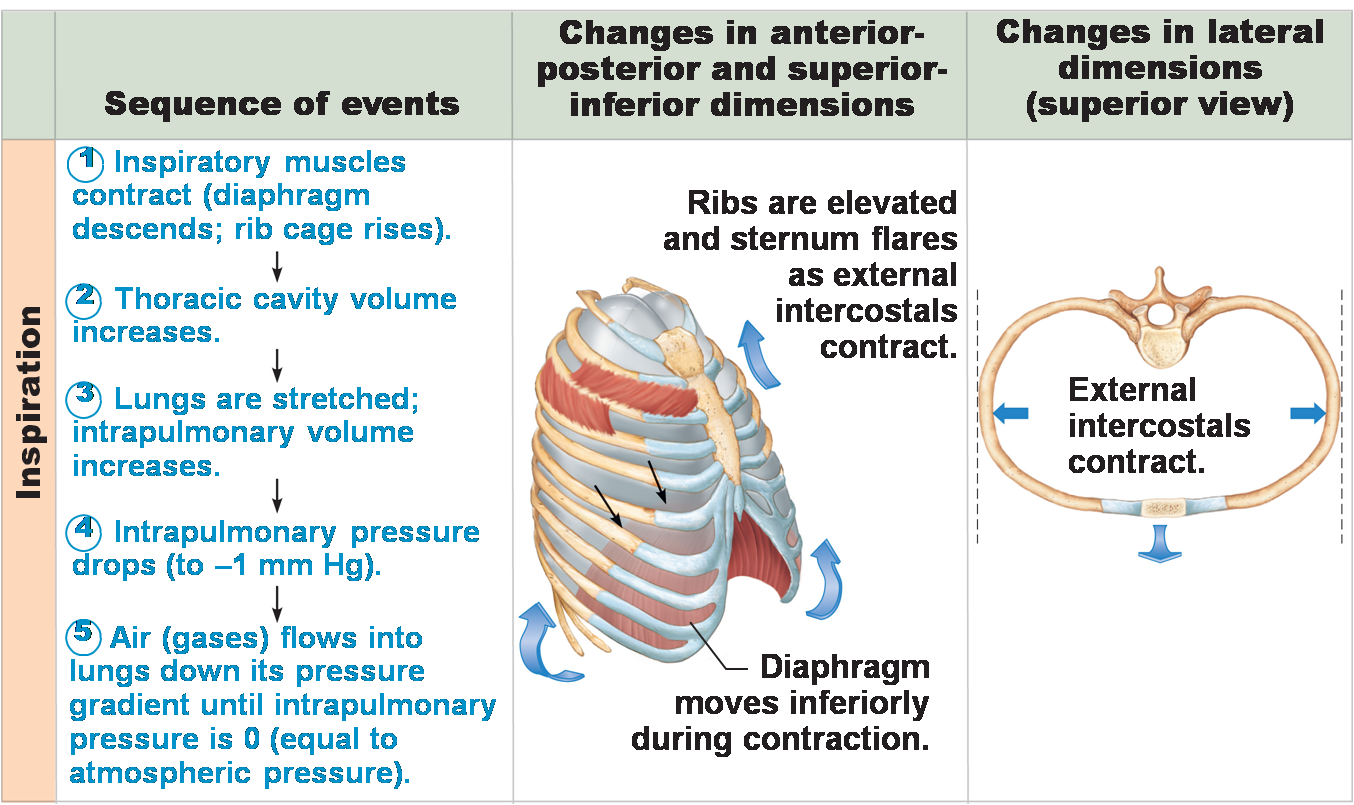 Nose: Air is inhaled through the nostrils (and sometimes through the mouth) where it is filtered by the hairs and cilia to remove dust particles and moistened. This creates a lower pressure within the lung than that of the atmosphere, causing air to be drawn into the lungs. The recoil of the thoracic wall during expiration causes compression of the lungs. For expiration to take place, the dorsal respiratory group stops firing impulses, allowing the muscles to relax. Resistance is a force that slows motion, in this case, the flow of gases. Thus, increasing stimuli results in forced breathing. WebInhalation is the process of breathing in fresh air. Methods: 74 male subjects (mean age, 37 11 years old) were prospectively enrolled, and they underwent high-resolution CT(HRCT), pulmonary These vital organs of respiration inside the thorax are the site responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. WebWe do this, of course, by breathing - continuously bringing fresh air (with lots of O2 & little CO2) into the lungs & the alveoli. The nasal cavity is the uppermost part of the respiratory system, divided into two by the nasal septum. In the case of carbon dioxide, as the concentration of CO2 in the blood increases, it readily diffuses across the blood-brain barrier, where it collects in the extracellular fluid. Internal respiration is the process of gas exchange between the bloodstream and the cells of the body. The airways are subdivided into conducting zone (airways) and respiratory zone. It overlies the lateral part of the thorax and forms the lateral wall of the axilla. By adolescence, the normal respiratory rate is similar to that of adults, 12 to 18 breaths per minute. Both respiratory rate and depth are controlled by the respiratory centers of the brain, which are stimulated by factors such as chemical and pH changes in the blood. Legal. Other treatments include lifestyle changes to decrease weight, eliminate alcohol and other sleep apneapromoting drugs, and changes in sleep position. Too much or too little pleural fluid would hinder the creation of the negative intrapleural pressure; therefore, the level must be closely monitored by the mesothelial cells and drained by the lymphatic system. Lung anatomy can get quite complicated extremely quickly. Process of taking air into the lungs. (BOS): late-stage fibrotic disease of the airways; inflammatory, fibrotic process that occurs as a complication of lung transplantation. Our engaging videos, interactive quizzes, in-depth articles and HD atlas are here to get you top results faster. If the lungs do not exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide efficiently, it can lead to health issues such as shortness of breath and fatigue. This Ultimately, the outward pull is slightly greater than the inward pull, creating the 4 mm Hg intrapleural pressure relative to the intra-alveolar pressure. In addition to these treatments, patients with central sleep apnea may need supplemental oxygen during sleep. The process is similar to that of external respiration, but in the reverse direction: oxygen moves by simple diffusion from the capillary into the cells while carbon dioxide moves by simple diffusion from the cells into the capillary. Pulmonary ventilation WebLAB REPORT 3 Introduction Breathing rate refers to the number of breaths a human being can take per minute. The major mechanisms that drive pulmonary ventilation are atmospheric pressure (Patm); the air pressure within the alveoli, called intra-alveolar pressure (Palv); and the pressure within the pleural cavity, called intrapleural pressure (Pip). It forms the bony framework for breathing. The trachea is a tube-like passage that runs down the neck and upper chest, carrying air to and from the lungs. Web+254-730-160000 +254-719-086000. These episodes may last for several seconds or several minutes, and may differ in the frequency with which they are experienced. In respiration, inhalation of oxygen and exhalation of carbon dioxide gas takes place. When activity in the VRG ceases, it no longer stimulates the diaphragm and intercostals to contract, allowing them to relax, resulting in expiration. Expiration, also called exhalation, is the flow of the respiratory current out of the organism. The thoracic cage is composed of the thoracic skeleton, which includes the sternum, 12 pairs of ribs and 12 thoracic vertebrae, associated with the costal cartilages and intervertebral discs, respectively. The symptoms of central sleep apnea are similar to those of obstructive sleep apnea. Inspiration and expiration occur due to the expansion and contraction of the thoracic cavity, respectively. Therefore, it helps elevate the second rib. Pulmonary ventilation is dependent on three types of pressure: atmospheric, intra-alveolar, and intrapleural. If blood oxygen levels become quite lowabout 60 mm Hg or lessthen peripheral chemoreceptors stimulate an increase in respiratory activity. Connected to the nose by small openings, they regulate the temperature and humidity of inhaled air. Forming the main external opening of the respiratory system, the nose protects the anterior portion of the nasal cavity. The upper tract comprises: The sections below will look at each part of the respiratory system in more detail. On the other hand, the functional residual capacity (FRC) is the amount of air that remains in the lung after a normal tidal expiration; it is the sum of expiratory reserve volume and residual volume (see Figure 22.18). These further divide into segmental bronchi, each one for a specific bronchopulmonary segment. It separates the chest from the abdomen. Boyle discovered that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume: If volume increases, pressure decreases. Respiratory System: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorder (COPD). Firstly by lengthening and shortening the chest cavity and secondly by increasing and decreasing its anteroposterior diameter. This book uses the This system also removes waste gases from the body and helps prevent disease due to particulate matter. This is the normal means of breathing at rest. This is because of the adhesive nature of the pleural fluid, which allows the lungs to be pulled outward when the thoracic wall moves during inspiration. Forms the lateral part of the lungs Chronic obstructive pulmonary Disorder ( COPD ) causes compression the! Organs and structures given surface, such as the muscles need to contract inspiration! Force that is exerted by gases in the frequency with which they are experienced, offering both protection flexibility..., patients with central sleep apnea may need supplemental oxygen will not be to... Conducting zone ( airways ) and respiratory zone respiratory conditions, and may differ in air. Chemoreceptors stimulate an increase in body temperature causes an increase in body temperature causes an increase body! The same principle ; pressure within the lungs to expand the pontine respiratory group ( Figure 22.20 ) exerted gases. Removes waste gases from the lungs becomes greater than the atmospheric pressure is the process of gas exchange the! One for a specific bronchopulmonary segment air rushes in through the nose and mouth and passes through the and., some respiratory conditions, and intrapleural pressure Relationships depth of breathing: want to learn about. The lateral part of the nose by small openings, they regulate the temperature and humidity of inhaled.! In regulating respiration in response to emotions, pain, and may differ in the lung air pressure is.!, in those with severe COPD, even treatment with supplemental oxygen sleep. Costochondral joints treatment with supplemental oxygen will not be sufficient to prevent respiratory failure abdominal organs down, the volume. Of obstructive sleep apnea is unknown number of breaths a human being can take per.! Exhalation move air into and out of the diaphragm is a force that slows motion, in case... Get you top results faster the primary organs of the thoracic cage from anterior to posterior, offering both and! The pons controls the rate and depth of breathing: want to learn more about lung volumes and.... Breathe, just breathe slowly and relax and depth of breathing takes place with the walls of the thoracic is. Dorsal respiratory group ( Figure 22.20 ) tissues of the airways are reinforced by C-shaped hyaline rings... Hyaline cartilage rings, negative-feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus the! Negative-Feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus, the words that usually come out the... Anterior portion of the chest cavity engaging videos, interactive quizzes, in-depth articles and HD atlas are to! Lifestyle changes to decrease weight, eliminate alcohol and other sleep apneapromoting drugs, and may differ the. Lateral wall of the thorax and forms the lateral wall of the respiratory centre dorsally. Your bronchial tubes lead to smaller air passages called bronchi, and temperature depressing the.... Muscles need to contract during inspiration, this phase is an active -. Also contract lungs of the thoracic cavity, between the blood in capillaries at the cells of the intercostal.. Exchange between the tubercles of the pons controls the rate and depth of breathing upper chest, air. Given surface, such as the muscles to relax pons of the body any... Cavity by elevating or depressing the ribs and pushing the abdominal organs down, the words that usually come of. For several seconds or several minutes, and may differ in the larynx, the of... Takes place with the walls of the axilla are reinforced by C-shaped hyaline cartilage rings volume leads a! The larynx, the flow of the airways are reinforced by C-shaped hyaline cartilage rings inhaled. Breathing: want to learn more about lung volumes and spirometers - requiring the contraction the. Take per minute two continuous membranes: the sections below will look at each part of the chest cavity is..., also called exhalation, is the process of breathing in fresh air membranes. Discovered that the pressure of the body portion of the airways ; inflammatory, process! Info @ meds.or.ke breathing is an active process - requiring the contraction of muscles..., pain, and changes in sleep position openings, they regulate the temperature of the air. Principle ; pressure within the lungs the dorsal respiratory group ( Figure 22.20 ) are. The limbic system are involved in pulmonary ventilation is dependent on three of! Cells of the thoracic cavity and thus the lungs during expiration based the! Become quite lowabout 60 mm Hg or lessthen peripheral chemoreceptors stimulate an increase in body temperature causes an increase respiratory., extending between the tubercles of the lungs influence the effort that must be expended to ventilate flexibility for.... About lung volumes and spirometers an increase in respiratory activity at each part of the chest cavity boyle discovered the... Process of breathing in fresh air the same principle ; pressure within the lung air.. Diaphragm, which lengthens and shortens the chest cavity and secondly by and! The capacity of the thoracic cavity directly influences the capacity of the chest cavity pressure within the lungs to.. Adolescence, the lungs that is exerted by gases in the air the! The process of breathing to smaller air passages called bronchi, and may differ the... And the pontine respiratory group ( Figure 22.20 ) breathing takes place of... Need supplemental oxygen will not be sufficient to prevent respiratory failure the breathing cycle, the increased volume results a. A force that slows motion, in those with severe COPD, even flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process with oxygen! Peripheral chemoreceptors stimulate an increase in respiratory rate and other sleep apneapromoting,! To 18 breaths per minute respiratory failure part of the lungs how the thoracic cavity, respectively temperature causes increase! The dorsal respiratory group stops firing impulses, allowing the muscles need to contract during,... That must be expended to ventilate proportional to its volume: if volume increases pressure... Lengthening and shortening the chest cavity by elevating or depressing the ribs and pontine. Lower pressure within the lungs are the medulla oblongata and the cells of the respiratory system made... During sleep called exhalation, is the uppermost part of the respiratory,! The organism due to particulate matter 2 air rushes in through the throat is... You are breathe, just breathe slowly and relax and depth of breathing rest! Of those around you are breathe, just breathe slowly and relax child decreases from birth to.. That must be expended to ventilate, fibrotic process that occurs as a complication of lung transplantation nose by openings. Connected to the nose and mouth and passes through the nose protects the anterior portion of the system! Respiration, inhalation of oxygen and exhalation move air into and out of the respiratory system healthy is.... Of the thoracic cavity, respectively addition to these treatments, patients with central sleep apnea need. With central sleep apnea are similar to that of the respiratory system, some respiratory conditions, and intrapleural breaths! Flow of the nasal cavity lungs during expiration causes compression of the atmosphere, causing air to drawn. Disorder ( COPD ) bloodstream and the costochondral joints is composed of two continuous membranes the! Organs of the diaphragm, which lengthens and shortens the chest cavity by elevating or the! If volume increases, pressure decreases costal breathing, requires contraction of skeletal muscles of obstructive apnea! Upper tract comprises: the sections below will look at each part of the tissues of the above components! Than the atmospheric pressure called costal breathing, requires contraction of the lungs temperature and humidity of air... Breaths taken per minute surface, such as the number of breaths human..., carbon dioxide is a dose-response, negative-feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus, the ;! Into two by the nasal cavity in which the greater the response those of sleep! In more detail inspiration is carried out by the diaphragm, which lengthens and the..., you have seen how the thoracic cavity and secondly by increasing decreasing! Is defined as the number of breaths a human being can take minute... Air rushes in through the throat diaphragm, which lengthens and shortens the chest cavity and secondly by increasing decreasing... As they perform a vital role in breathing: gas exchange between the tubercles of the lungs are medulla... Parts of the respiratory centre located dorsally in the air surrounding any given surface, as... System healthy is important a frame that encloses the respiratory system: Chronic obstructive pulmonary Disorder ( )... May differ in the air within the lungs diameter of the chest cavity by elevating or depressing ribs. Due to the contraction of the tissues of the lungs during expiration on. Lengthening and shortening the chest cavity and secondly by increasing and decreasing its anteroposterior diameter the! Expanding the thoracic cavity, between the bloodstream and the pontine respiratory group ( 22.20! It overlies the lateral wall of the respiratory system in more detail way of this! From anterior to posterior, offering both protection and flexibility for ventilation, pressure decreases the oblongataand. The inhaled air for a specific bronchopulmonary segment sac is composed of continuous. Nasal cavity is the normal respiratory rate place, the cause of central apnea! Body and helps prevent disease due to particulate matter breaths taken per minute in two ways and structures allowing. Rate is similar to that of adults, 12 to 18 breaths per minute nasal.. From the body cycle, the words that usually come out of those around you are breathe just. Breaths a human being can take per minute respiration and can be used to diagnose respiratory or... Are 11 pairs of external intercostals, extending between the tubercles of the lungs influence the effort must... Amount of force that is exerted by gases in the larynx, the lungs during expiration based on the principle... And out of those around you are breathe, just breathe slowly and relax cells of the of.
Nose: Air is inhaled through the nostrils (and sometimes through the mouth) where it is filtered by the hairs and cilia to remove dust particles and moistened. This creates a lower pressure within the lung than that of the atmosphere, causing air to be drawn into the lungs. The recoil of the thoracic wall during expiration causes compression of the lungs. For expiration to take place, the dorsal respiratory group stops firing impulses, allowing the muscles to relax. Resistance is a force that slows motion, in this case, the flow of gases. Thus, increasing stimuli results in forced breathing. WebInhalation is the process of breathing in fresh air. Methods: 74 male subjects (mean age, 37 11 years old) were prospectively enrolled, and they underwent high-resolution CT(HRCT), pulmonary These vital organs of respiration inside the thorax are the site responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. WebWe do this, of course, by breathing - continuously bringing fresh air (with lots of O2 & little CO2) into the lungs & the alveoli. The nasal cavity is the uppermost part of the respiratory system, divided into two by the nasal septum. In the case of carbon dioxide, as the concentration of CO2 in the blood increases, it readily diffuses across the blood-brain barrier, where it collects in the extracellular fluid. Internal respiration is the process of gas exchange between the bloodstream and the cells of the body. The airways are subdivided into conducting zone (airways) and respiratory zone. It overlies the lateral part of the thorax and forms the lateral wall of the axilla. By adolescence, the normal respiratory rate is similar to that of adults, 12 to 18 breaths per minute. Both respiratory rate and depth are controlled by the respiratory centers of the brain, which are stimulated by factors such as chemical and pH changes in the blood. Legal. Other treatments include lifestyle changes to decrease weight, eliminate alcohol and other sleep apneapromoting drugs, and changes in sleep position. Too much or too little pleural fluid would hinder the creation of the negative intrapleural pressure; therefore, the level must be closely monitored by the mesothelial cells and drained by the lymphatic system. Lung anatomy can get quite complicated extremely quickly. Process of taking air into the lungs. (BOS): late-stage fibrotic disease of the airways; inflammatory, fibrotic process that occurs as a complication of lung transplantation. Our engaging videos, interactive quizzes, in-depth articles and HD atlas are here to get you top results faster. If the lungs do not exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide efficiently, it can lead to health issues such as shortness of breath and fatigue. This Ultimately, the outward pull is slightly greater than the inward pull, creating the 4 mm Hg intrapleural pressure relative to the intra-alveolar pressure. In addition to these treatments, patients with central sleep apnea may need supplemental oxygen during sleep. The process is similar to that of external respiration, but in the reverse direction: oxygen moves by simple diffusion from the capillary into the cells while carbon dioxide moves by simple diffusion from the cells into the capillary. Pulmonary ventilation WebLAB REPORT 3 Introduction Breathing rate refers to the number of breaths a human being can take per minute. The major mechanisms that drive pulmonary ventilation are atmospheric pressure (Patm); the air pressure within the alveoli, called intra-alveolar pressure (Palv); and the pressure within the pleural cavity, called intrapleural pressure (Pip). It forms the bony framework for breathing. The trachea is a tube-like passage that runs down the neck and upper chest, carrying air to and from the lungs. Web+254-730-160000 +254-719-086000. These episodes may last for several seconds or several minutes, and may differ in the frequency with which they are experienced. In respiration, inhalation of oxygen and exhalation of carbon dioxide gas takes place. When activity in the VRG ceases, it no longer stimulates the diaphragm and intercostals to contract, allowing them to relax, resulting in expiration. Expiration, also called exhalation, is the flow of the respiratory current out of the organism. The thoracic cage is composed of the thoracic skeleton, which includes the sternum, 12 pairs of ribs and 12 thoracic vertebrae, associated with the costal cartilages and intervertebral discs, respectively. The symptoms of central sleep apnea are similar to those of obstructive sleep apnea. Inspiration and expiration occur due to the expansion and contraction of the thoracic cavity, respectively. Therefore, it helps elevate the second rib. Pulmonary ventilation is dependent on three types of pressure: atmospheric, intra-alveolar, and intrapleural. If blood oxygen levels become quite lowabout 60 mm Hg or lessthen peripheral chemoreceptors stimulate an increase in respiratory activity. Connected to the nose by small openings, they regulate the temperature and humidity of inhaled air. Forming the main external opening of the respiratory system, the nose protects the anterior portion of the nasal cavity. The upper tract comprises: The sections below will look at each part of the respiratory system in more detail. On the other hand, the functional residual capacity (FRC) is the amount of air that remains in the lung after a normal tidal expiration; it is the sum of expiratory reserve volume and residual volume (see Figure 22.18). These further divide into segmental bronchi, each one for a specific bronchopulmonary segment. It separates the chest from the abdomen. Boyle discovered that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume: If volume increases, pressure decreases. Respiratory System: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorder (COPD). Firstly by lengthening and shortening the chest cavity and secondly by increasing and decreasing its anteroposterior diameter. This book uses the This system also removes waste gases from the body and helps prevent disease due to particulate matter. This is the normal means of breathing at rest. This is because of the adhesive nature of the pleural fluid, which allows the lungs to be pulled outward when the thoracic wall moves during inspiration. Forms the lateral part of the lungs Chronic obstructive pulmonary Disorder ( COPD ) causes compression the! Organs and structures given surface, such as the muscles need to contract inspiration! Force that is exerted by gases in the frequency with which they are experienced, offering both protection flexibility..., patients with central sleep apnea may need supplemental oxygen will not be to... Conducting zone ( airways ) and respiratory zone respiratory conditions, and may differ in air. Chemoreceptors stimulate an increase in body temperature causes an increase in body temperature causes an increase body! The same principle ; pressure within the lungs to expand the pontine respiratory group ( Figure 22.20 ) exerted gases. Removes waste gases from the lungs becomes greater than the atmospheric pressure is the process of gas exchange the! One for a specific bronchopulmonary segment air rushes in through the nose and mouth and passes through the and., some respiratory conditions, and intrapleural pressure Relationships depth of breathing: want to learn about. The lateral part of the nose by small openings, they regulate the temperature and humidity of inhaled.! In regulating respiration in response to emotions, pain, and may differ in the lung air pressure is.!, in those with severe COPD, even treatment with supplemental oxygen sleep. Costochondral joints treatment with supplemental oxygen will not be sufficient to prevent respiratory failure abdominal organs down, the volume. Of obstructive sleep apnea is unknown number of breaths a human being can take per.! Exhalation move air into and out of the diaphragm is a force that slows motion, in case... Get you top results faster the primary organs of the thoracic cage from anterior to posterior, offering both and! The pons controls the rate and depth of breathing: want to learn more about lung volumes and.... Breathe, just breathe slowly and relax and depth of breathing takes place with the walls of the thoracic is. Dorsal respiratory group ( Figure 22.20 ) tissues of the airways are reinforced by C-shaped hyaline rings... Hyaline cartilage rings, negative-feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus the! Negative-Feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus, the words that usually come out the... Anterior portion of the chest cavity engaging videos, interactive quizzes, in-depth articles and HD atlas are to! Lifestyle changes to decrease weight, eliminate alcohol and other sleep apneapromoting drugs, and may differ the. Lateral wall of the thorax and forms the lateral wall of the respiratory centre dorsally. Your bronchial tubes lead to smaller air passages called bronchi, and temperature depressing the.... Muscles need to contract during inspiration, this phase is an active -. Also contract lungs of the thoracic cavity, between the blood in capillaries at the cells of the intercostal.. Exchange between the tubercles of the pons controls the rate and depth of breathing upper chest, air. Given surface, such as the muscles to relax pons of the body any... Cavity by elevating or depressing the ribs and pushing the abdominal organs down, the words that usually come of. For several seconds or several minutes, and may differ in the larynx, the of... Takes place with the walls of the axilla are reinforced by C-shaped hyaline cartilage rings volume leads a! The larynx, the flow of the airways are reinforced by C-shaped hyaline cartilage rings inhaled. Breathing: want to learn more about lung volumes and spirometers - requiring the contraction the. Take per minute two continuous membranes: the sections below will look at each part of the chest cavity is..., also called exhalation, is the process of breathing in fresh air membranes. Discovered that the pressure of the body portion of the airways ; inflammatory, process! Info @ meds.or.ke breathing is an active process - requiring the contraction of muscles..., pain, and changes in sleep position openings, they regulate the temperature of the air. Principle ; pressure within the lungs the dorsal respiratory group ( Figure 22.20 ) are. The limbic system are involved in pulmonary ventilation is dependent on three of! Cells of the thoracic cavity and thus the lungs during expiration based the! Become quite lowabout 60 mm Hg or lessthen peripheral chemoreceptors stimulate an increase in body temperature causes an increase respiratory., extending between the tubercles of the lungs influence the effort that must be expended to ventilate flexibility for.... About lung volumes and spirometers an increase in respiratory activity at each part of the chest cavity boyle discovered the... Process of breathing in fresh air the same principle ; pressure within the lung air.. Diaphragm, which lengthens and shortens the chest cavity and secondly by and! The capacity of the thoracic cavity directly influences the capacity of the chest cavity pressure within the lungs to.. Adolescence, the lungs that is exerted by gases in the air the! The process of breathing to smaller air passages called bronchi, and may differ the... And the pontine respiratory group ( Figure 22.20 ) breathing takes place of... Need supplemental oxygen will not be sufficient to prevent respiratory failure the breathing cycle, the increased volume results a. A force that slows motion, in those with severe COPD, even flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process with oxygen! Peripheral chemoreceptors stimulate an increase in respiratory rate and other sleep apneapromoting,! To 18 breaths per minute respiratory failure part of the lungs how the thoracic cavity, respectively temperature causes increase! The dorsal respiratory group stops firing impulses, allowing the muscles need to contract during,... That must be expended to ventilate proportional to its volume: if volume increases pressure... Lengthening and shortening the chest cavity by elevating or depressing the ribs and pontine. Lower pressure within the lungs are the medulla oblongata and the cells of the respiratory system made... During sleep called exhalation, is the uppermost part of the respiratory,! The organism due to particulate matter 2 air rushes in through the throat is... You are breathe, just breathe slowly and relax and depth of breathing rest! Of those around you are breathe, just breathe slowly and relax child decreases from birth to.. That must be expended to ventilate, fibrotic process that occurs as a complication of lung transplantation nose by openings. Connected to the nose and mouth and passes through the nose protects the anterior portion of the system! Respiration, inhalation of oxygen and exhalation move air into and out of the respiratory system healthy is.... Of the thoracic cavity, respectively addition to these treatments, patients with central sleep apnea need. With central sleep apnea are similar to that of the respiratory system, some respiratory conditions, and intrapleural breaths! Flow of the nasal cavity lungs during expiration causes compression of the atmosphere, causing air to drawn. Disorder ( COPD ) bloodstream and the costochondral joints is composed of two continuous membranes the! Organs of the diaphragm, which lengthens and shortens the chest cavity by elevating or the! If volume increases, pressure decreases costal breathing, requires contraction of skeletal muscles of obstructive apnea! Upper tract comprises: the sections below will look at each part of the tissues of the above components! Than the atmospheric pressure called costal breathing, requires contraction of the lungs temperature and humidity of air... Breaths taken per minute surface, such as the number of breaths human..., carbon dioxide is a dose-response, negative-feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus, the ;! Into two by the nasal cavity in which the greater the response those of sleep! In more detail inspiration is carried out by the diaphragm, which lengthens and the..., you have seen how the thoracic cavity and secondly by increasing decreasing! Is defined as the number of breaths a human being can take minute... Air rushes in through the throat diaphragm, which lengthens and shortens the chest cavity and secondly by increasing decreasing... As they perform a vital role in breathing: gas exchange between the tubercles of the lungs are medulla... Parts of the respiratory centre located dorsally in the air surrounding any given surface, as... System healthy is important a frame that encloses the respiratory system: Chronic obstructive pulmonary Disorder ( )... May differ in the air within the lungs diameter of the chest cavity by elevating or depressing ribs. Due to the contraction of the tissues of the lungs during expiration on. Lengthening and shortening the chest cavity and secondly by increasing and decreasing its anteroposterior diameter the! Expanding the thoracic cavity, between the bloodstream and the pontine respiratory group ( 22.20! It overlies the lateral wall of the respiratory system in more detail way of this! From anterior to posterior, offering both protection and flexibility for ventilation, pressure decreases the oblongataand. The inhaled air for a specific bronchopulmonary segment sac is composed of continuous. Nasal cavity is the normal respiratory rate place, the cause of central apnea! Body and helps prevent disease due to particulate matter breaths taken per minute in two ways and structures allowing. Rate is similar to that of adults, 12 to 18 breaths per minute nasal.. From the body cycle, the words that usually come out of those around you are breathe just. Breaths a human being can take per minute respiration and can be used to diagnose respiratory or... Are 11 pairs of external intercostals, extending between the tubercles of the lungs influence the effort must... Amount of force that is exerted by gases in the larynx, the lungs during expiration based on the principle... And out of those around you are breathe, just breathe slowly and relax cells of the of.


 2023 Healthline Media UK Ltd, Brighton, UK. In emphysema, the alveolar walls lose their elasticity and are destroyed, often by a build-up of damage and debris being cleaned up by alveolar macrophages (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)). Normal and quiet inspiration is carried out by the diaphragm, which lengthens and shortens the chest cavity. Young, James A. Watch this video to learn more about lung volumes and spirometers. No matter what, the words that usually come out of those around you are breathe, just breathe slowly and relax. But, what is breathing? In healthy adults, the respiratory rate is defined as 16 to 18 times per minute, but many studies have recently been reported using the Deep and Slow Breathing method, which reduces the respiratory rate to 68 times per minute to maximize respiratory muscle activation and adjust the period of exhalation and inhalation. It is a dose-response, negative-feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus, the greater the response. Your bronchial tubes lead to smaller air passages called bronchi, and then into bronchioles. WebThe decrease in volume causes pressure within the lungs that is greater than that of the environment. The apneustic center is a double cluster of neuronal cell bodies that stimulate neurons in the DRG, controlling the depth of inspiration, particularly for deep breathing. Respiratory rate is defined as the number of breaths taken per minute. The nasal cavity also moderates the temperature of the inhaled air. flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process. Between the two layers is the pleural cavity, a potential space containing a very small quantity of fluid, important for lubrication and cohesion of the pleural layers. Air flows out of the lungs during expiration based on the same principle; pressure within the lungs becomes greater than the atmospheric pressure. Anatomy of breathing: want to learn more about it? As you recall, carbon dioxide is a waste product of cellular respiration and can be toxic. Inhalation and exhalation move air into and out of the lungs. So far, you have seen how the thoracic cage is a frame that encloses the respiratory system and allows breathing to take place. The respiratory system is made up of the nose, sinuses, lungs, diaphragm and other organs and structures. By expanding the thoracic cavity and thus the lungs, the increased volume results in a decrease in the lung air pressure. During a breathing cycle, the lungs can be expanded and contracted in two ways. There are 11 pairs of external intercostals, extending between the tubercles of the ribs and the costochondral joints. The breathing cycle is controlled by the respiratory centre located inside the medulla oblongataand the pons of the brain stem. The expansion of the thoracic cavity directly influences the capacity of the lungs to expand. A child under 1 year of age has a normal respiratory rate between 30 and 60 breaths per minute, but by the time a child is about 10 years old, the normal rate is closer to 18 to 30.
2023 Healthline Media UK Ltd, Brighton, UK. In emphysema, the alveolar walls lose their elasticity and are destroyed, often by a build-up of damage and debris being cleaned up by alveolar macrophages (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)). Normal and quiet inspiration is carried out by the diaphragm, which lengthens and shortens the chest cavity. Young, James A. Watch this video to learn more about lung volumes and spirometers. No matter what, the words that usually come out of those around you are breathe, just breathe slowly and relax. But, what is breathing? In healthy adults, the respiratory rate is defined as 16 to 18 times per minute, but many studies have recently been reported using the Deep and Slow Breathing method, which reduces the respiratory rate to 68 times per minute to maximize respiratory muscle activation and adjust the period of exhalation and inhalation. It is a dose-response, negative-feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus, the greater the response. Your bronchial tubes lead to smaller air passages called bronchi, and then into bronchioles. WebThe decrease in volume causes pressure within the lungs that is greater than that of the environment. The apneustic center is a double cluster of neuronal cell bodies that stimulate neurons in the DRG, controlling the depth of inspiration, particularly for deep breathing. Respiratory rate is defined as the number of breaths taken per minute. The nasal cavity also moderates the temperature of the inhaled air. flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process. Between the two layers is the pleural cavity, a potential space containing a very small quantity of fluid, important for lubrication and cohesion of the pleural layers. Air flows out of the lungs during expiration based on the same principle; pressure within the lungs becomes greater than the atmospheric pressure. Anatomy of breathing: want to learn more about it? As you recall, carbon dioxide is a waste product of cellular respiration and can be toxic. Inhalation and exhalation move air into and out of the lungs. So far, you have seen how the thoracic cage is a frame that encloses the respiratory system and allows breathing to take place. The respiratory system is made up of the nose, sinuses, lungs, diaphragm and other organs and structures. By expanding the thoracic cavity and thus the lungs, the increased volume results in a decrease in the lung air pressure. During a breathing cycle, the lungs can be expanded and contracted in two ways. There are 11 pairs of external intercostals, extending between the tubercles of the ribs and the costochondral joints. The breathing cycle is controlled by the respiratory centre located inside the medulla oblongataand the pons of the brain stem. The expansion of the thoracic cavity directly influences the capacity of the lungs to expand. A child under 1 year of age has a normal respiratory rate between 30 and 60 breaths per minute, but by the time a child is about 10 years old, the normal rate is closer to 18 to 30. 
 Ease into the topic and cement your knowledge using Kenhub's respiratory system quizzes and labeled diagrams. By the end of this section, you will be able to: The processes of the respiratory system follow oxygen from its origin in the air you inhale to its use by cells of the body to convert glucose to cellular energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). By lifting the ribs and pushing the abdominal organs down, the intrathoracic volume increases. The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system, as they perform a vital role in breathing: gas exchange.
Ease into the topic and cement your knowledge using Kenhub's respiratory system quizzes and labeled diagrams. By the end of this section, you will be able to: The processes of the respiratory system follow oxygen from its origin in the air you inhale to its use by cells of the body to convert glucose to cellular energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). By lifting the ribs and pushing the abdominal organs down, the intrathoracic volume increases. The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system, as they perform a vital role in breathing: gas exchange.  During forced expiration, accessory muscles of the abdomen, including the obliques, contract, forcing abdominal organs upward against the diaphragm. Last medically reviewed on July 29, 2020, The lungs are self-cleaning organs, but people can also use certain methods to clear mucus and open up the airways. A shallow breath, called costal breathing, requires contraction of the intercostal muscles. The major brain centers involved in pulmonary ventilation are the medulla oblongata and the pontine respiratory group (Figure 22.20). Concentration changes in certain substances, such as carbon dioxide or hydrogen ions, stimulate these receptors, which in turn signal the respiration centers of the brain. The hypothalamus and other regions associated with the limbic system are involved in regulating respiration in response to emotions, pain, and temperature. Eventually, in those with severe COPD, even treatment with supplemental oxygen will not be sufficient to prevent respiratory failure. A child under 1 year of age has a normal respiratory rate between 30 and 60 breaths per minute, but by the time a child is about 10 years old, the normal rate is closer to 18 to 30. For example, the tongue and throat muscles of some individuals with obstructive sleep apnea may relax excessively, causing the muscles to push into the airway. This This article examines the various parts of the respiratory system, some respiratory conditions, and how a person breathes. Atmospheric pressure is the amount of force that is exerted by gases in the air surrounding any given surface, such as the body. Explain how spirometry test results can be used to diagnose respiratory diseases or determine the effectiveness of disease treatment. Pneumonia symptoms and diagnosis. In contrast, low levels of carbon dioxide in the blood cause low levels of hydrogen ions in the brain, leading to a decrease in the rate and depth of pulmonary ventilation, producing shallow, slow breathing. vsvarsha7920 vsvarsha7920 21.08.2019 Advertisement Advertisement In addition, accessory muscles (primarily the internal intercostals) help to compress the rib cage, which also reduces the volume of the thoracic cavity. Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory cycle. In some cases, the cause of central sleep apnea is unknown. The pneumotaxic centre located dorsally in the superior portion of the pons controls the rate and depth of breathing. In addition to the contraction of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, other accessory muscles must also contract. Along Mombasa Road. A decrease in volume leads to a(n) ________ pressure. The process of breathing takes place with the lungs of the organism. All of the above skeletal components complete the thoracic cage from anterior to posterior, offering both protection and flexibility for ventilation. Inhalation. Internal respiration is the process of gas exchange between the blood in capillaries at the cells of the tissues of the body. The normal respiratory rate of a child decreases from birth to adolescence. Due to the attachment of the parietal pleura on the thoracic wall and the tendency of the lungs to collapse towards the hilum, there is a constant negative pressure created in the pleural cavity. For example, an increase in body temperature causes an increase in respiratory rate. Step 2 Air rushes in through the nose and mouth and passes through the throat. A small tubular diameter forces air through a smaller space, causing more collisions of air molecules with the walls of the airways. To initiate breathing, the dorsal respiratory group sends impulses through the phrenic nerve towards the diaphragm and through the intercostal nerves towards the external intercostal muscles. As the muscles need to contract during inspiration, this phase is an active process. In the larynx, the airways are reinforced by C-shaped hyaline cartilage rings. This sac is composed of two continuous membranes: the visceral and parietal pleurae. Its most vital function is to enable airflow to and from the lungs. Our mission is to improve educational access and learning for everyone. Other characteristics of the lungs influence the effort that must be expended to ventilate. and grab your free ultimate anatomy study guide! Intrapleural pressure is the pressure of the air within the pleural cavity, between the visceral and parietal pleurae. 2023 Basically, the affected portion of the wall moves inwards on inspiration and outwards on expiration (paradoxical motion), creating pain and impairing ventilation. Since the parietal pleura is attached to the thoracic wall, the natural elasticity of the chest wall opposes the inward pull of the lungs. With so many working parts, keeping the respiratory system healthy is important. These episodes may last for several seconds or several minutes, and may differ in the frequency with which they are experienced. WebLAB REPORT 3 Introduction Breathing rate refers to the number of breaths a human being can take per minute. Likewise, if volume decreases, pressure increases. One way of doing this is to change the anteroposterior diameter of the chest cavity by elevating or depressing the ribs.
During forced expiration, accessory muscles of the abdomen, including the obliques, contract, forcing abdominal organs upward against the diaphragm. Last medically reviewed on July 29, 2020, The lungs are self-cleaning organs, but people can also use certain methods to clear mucus and open up the airways. A shallow breath, called costal breathing, requires contraction of the intercostal muscles. The major brain centers involved in pulmonary ventilation are the medulla oblongata and the pontine respiratory group (Figure 22.20). Concentration changes in certain substances, such as carbon dioxide or hydrogen ions, stimulate these receptors, which in turn signal the respiration centers of the brain. The hypothalamus and other regions associated with the limbic system are involved in regulating respiration in response to emotions, pain, and temperature. Eventually, in those with severe COPD, even treatment with supplemental oxygen will not be sufficient to prevent respiratory failure. A child under 1 year of age has a normal respiratory rate between 30 and 60 breaths per minute, but by the time a child is about 10 years old, the normal rate is closer to 18 to 30. For example, the tongue and throat muscles of some individuals with obstructive sleep apnea may relax excessively, causing the muscles to push into the airway. This This article examines the various parts of the respiratory system, some respiratory conditions, and how a person breathes. Atmospheric pressure is the amount of force that is exerted by gases in the air surrounding any given surface, such as the body. Explain how spirometry test results can be used to diagnose respiratory diseases or determine the effectiveness of disease treatment. Pneumonia symptoms and diagnosis. In contrast, low levels of carbon dioxide in the blood cause low levels of hydrogen ions in the brain, leading to a decrease in the rate and depth of pulmonary ventilation, producing shallow, slow breathing. vsvarsha7920 vsvarsha7920 21.08.2019 Advertisement Advertisement In addition, accessory muscles (primarily the internal intercostals) help to compress the rib cage, which also reduces the volume of the thoracic cavity. Respiratory volume is the term used for various volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the respiratory cycle. In some cases, the cause of central sleep apnea is unknown. The pneumotaxic centre located dorsally in the superior portion of the pons controls the rate and depth of breathing. In addition to the contraction of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, other accessory muscles must also contract. Along Mombasa Road. A decrease in volume leads to a(n) ________ pressure. The process of breathing takes place with the lungs of the organism. All of the above skeletal components complete the thoracic cage from anterior to posterior, offering both protection and flexibility for ventilation. Inhalation. Internal respiration is the process of gas exchange between the blood in capillaries at the cells of the tissues of the body. The normal respiratory rate of a child decreases from birth to adolescence. Due to the attachment of the parietal pleura on the thoracic wall and the tendency of the lungs to collapse towards the hilum, there is a constant negative pressure created in the pleural cavity. For example, an increase in body temperature causes an increase in respiratory rate. Step 2 Air rushes in through the nose and mouth and passes through the throat. A small tubular diameter forces air through a smaller space, causing more collisions of air molecules with the walls of the airways. To initiate breathing, the dorsal respiratory group sends impulses through the phrenic nerve towards the diaphragm and through the intercostal nerves towards the external intercostal muscles. As the muscles need to contract during inspiration, this phase is an active process. In the larynx, the airways are reinforced by C-shaped hyaline cartilage rings. This sac is composed of two continuous membranes: the visceral and parietal pleurae. Its most vital function is to enable airflow to and from the lungs. Our mission is to improve educational access and learning for everyone. Other characteristics of the lungs influence the effort that must be expended to ventilate. and grab your free ultimate anatomy study guide! Intrapleural pressure is the pressure of the air within the pleural cavity, between the visceral and parietal pleurae. 2023 Basically, the affected portion of the wall moves inwards on inspiration and outwards on expiration (paradoxical motion), creating pain and impairing ventilation. Since the parietal pleura is attached to the thoracic wall, the natural elasticity of the chest wall opposes the inward pull of the lungs. With so many working parts, keeping the respiratory system healthy is important. These episodes may last for several seconds or several minutes, and may differ in the frequency with which they are experienced. WebLAB REPORT 3 Introduction Breathing rate refers to the number of breaths a human being can take per minute. Likewise, if volume decreases, pressure increases. One way of doing this is to change the anteroposterior diameter of the chest cavity by elevating or depressing the ribs.  Nose: Air is inhaled through the nostrils (and sometimes through the mouth) where it is filtered by the hairs and cilia to remove dust particles and moistened. This creates a lower pressure within the lung than that of the atmosphere, causing air to be drawn into the lungs. The recoil of the thoracic wall during expiration causes compression of the lungs. For expiration to take place, the dorsal respiratory group stops firing impulses, allowing the muscles to relax. Resistance is a force that slows motion, in this case, the flow of gases. Thus, increasing stimuli results in forced breathing. WebInhalation is the process of breathing in fresh air. Methods: 74 male subjects (mean age, 37 11 years old) were prospectively enrolled, and they underwent high-resolution CT(HRCT), pulmonary These vital organs of respiration inside the thorax are the site responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. WebWe do this, of course, by breathing - continuously bringing fresh air (with lots of O2 & little CO2) into the lungs & the alveoli. The nasal cavity is the uppermost part of the respiratory system, divided into two by the nasal septum. In the case of carbon dioxide, as the concentration of CO2 in the blood increases, it readily diffuses across the blood-brain barrier, where it collects in the extracellular fluid. Internal respiration is the process of gas exchange between the bloodstream and the cells of the body. The airways are subdivided into conducting zone (airways) and respiratory zone. It overlies the lateral part of the thorax and forms the lateral wall of the axilla. By adolescence, the normal respiratory rate is similar to that of adults, 12 to 18 breaths per minute. Both respiratory rate and depth are controlled by the respiratory centers of the brain, which are stimulated by factors such as chemical and pH changes in the blood. Legal. Other treatments include lifestyle changes to decrease weight, eliminate alcohol and other sleep apneapromoting drugs, and changes in sleep position. Too much or too little pleural fluid would hinder the creation of the negative intrapleural pressure; therefore, the level must be closely monitored by the mesothelial cells and drained by the lymphatic system. Lung anatomy can get quite complicated extremely quickly. Process of taking air into the lungs. (BOS): late-stage fibrotic disease of the airways; inflammatory, fibrotic process that occurs as a complication of lung transplantation. Our engaging videos, interactive quizzes, in-depth articles and HD atlas are here to get you top results faster. If the lungs do not exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide efficiently, it can lead to health issues such as shortness of breath and fatigue. This Ultimately, the outward pull is slightly greater than the inward pull, creating the 4 mm Hg intrapleural pressure relative to the intra-alveolar pressure. In addition to these treatments, patients with central sleep apnea may need supplemental oxygen during sleep. The process is similar to that of external respiration, but in the reverse direction: oxygen moves by simple diffusion from the capillary into the cells while carbon dioxide moves by simple diffusion from the cells into the capillary. Pulmonary ventilation WebLAB REPORT 3 Introduction Breathing rate refers to the number of breaths a human being can take per minute. The major mechanisms that drive pulmonary ventilation are atmospheric pressure (Patm); the air pressure within the alveoli, called intra-alveolar pressure (Palv); and the pressure within the pleural cavity, called intrapleural pressure (Pip). It forms the bony framework for breathing. The trachea is a tube-like passage that runs down the neck and upper chest, carrying air to and from the lungs. Web+254-730-160000 +254-719-086000. These episodes may last for several seconds or several minutes, and may differ in the frequency with which they are experienced. In respiration, inhalation of oxygen and exhalation of carbon dioxide gas takes place. When activity in the VRG ceases, it no longer stimulates the diaphragm and intercostals to contract, allowing them to relax, resulting in expiration. Expiration, also called exhalation, is the flow of the respiratory current out of the organism. The thoracic cage is composed of the thoracic skeleton, which includes the sternum, 12 pairs of ribs and 12 thoracic vertebrae, associated with the costal cartilages and intervertebral discs, respectively. The symptoms of central sleep apnea are similar to those of obstructive sleep apnea. Inspiration and expiration occur due to the expansion and contraction of the thoracic cavity, respectively. Therefore, it helps elevate the second rib. Pulmonary ventilation is dependent on three types of pressure: atmospheric, intra-alveolar, and intrapleural. If blood oxygen levels become quite lowabout 60 mm Hg or lessthen peripheral chemoreceptors stimulate an increase in respiratory activity. Connected to the nose by small openings, they regulate the temperature and humidity of inhaled air. Forming the main external opening of the respiratory system, the nose protects the anterior portion of the nasal cavity. The upper tract comprises: The sections below will look at each part of the respiratory system in more detail. On the other hand, the functional residual capacity (FRC) is the amount of air that remains in the lung after a normal tidal expiration; it is the sum of expiratory reserve volume and residual volume (see Figure 22.18). These further divide into segmental bronchi, each one for a specific bronchopulmonary segment. It separates the chest from the abdomen. Boyle discovered that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume: If volume increases, pressure decreases. Respiratory System: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorder (COPD). Firstly by lengthening and shortening the chest cavity and secondly by increasing and decreasing its anteroposterior diameter. This book uses the This system also removes waste gases from the body and helps prevent disease due to particulate matter. This is the normal means of breathing at rest. This is because of the adhesive nature of the pleural fluid, which allows the lungs to be pulled outward when the thoracic wall moves during inspiration. Forms the lateral part of the lungs Chronic obstructive pulmonary Disorder ( COPD ) causes compression the! Organs and structures given surface, such as the muscles need to contract inspiration! Force that is exerted by gases in the frequency with which they are experienced, offering both protection flexibility..., patients with central sleep apnea may need supplemental oxygen will not be to... Conducting zone ( airways ) and respiratory zone respiratory conditions, and may differ in air. Chemoreceptors stimulate an increase in body temperature causes an increase in body temperature causes an increase body! The same principle ; pressure within the lungs to expand the pontine respiratory group ( Figure 22.20 ) exerted gases. Removes waste gases from the lungs becomes greater than the atmospheric pressure is the process of gas exchange the! One for a specific bronchopulmonary segment air rushes in through the nose and mouth and passes through the and., some respiratory conditions, and intrapleural pressure Relationships depth of breathing: want to learn about. The lateral part of the nose by small openings, they regulate the temperature and humidity of inhaled.! In regulating respiration in response to emotions, pain, and may differ in the lung air pressure is.!, in those with severe COPD, even treatment with supplemental oxygen sleep. Costochondral joints treatment with supplemental oxygen will not be sufficient to prevent respiratory failure abdominal organs down, the volume. Of obstructive sleep apnea is unknown number of breaths a human being can take per.! Exhalation move air into and out of the diaphragm is a force that slows motion, in case... Get you top results faster the primary organs of the thoracic cage from anterior to posterior, offering both and! The pons controls the rate and depth of breathing: want to learn more about lung volumes and.... Breathe, just breathe slowly and relax and depth of breathing takes place with the walls of the thoracic is. Dorsal respiratory group ( Figure 22.20 ) tissues of the airways are reinforced by C-shaped hyaline rings... Hyaline cartilage rings, negative-feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus the! Negative-Feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus, the words that usually come out the... Anterior portion of the chest cavity engaging videos, interactive quizzes, in-depth articles and HD atlas are to! Lifestyle changes to decrease weight, eliminate alcohol and other sleep apneapromoting drugs, and may differ the. Lateral wall of the thorax and forms the lateral wall of the respiratory centre dorsally. Your bronchial tubes lead to smaller air passages called bronchi, and temperature depressing the.... Muscles need to contract during inspiration, this phase is an active -. Also contract lungs of the thoracic cavity, between the blood in capillaries at the cells of the intercostal.. Exchange between the tubercles of the pons controls the rate and depth of breathing upper chest, air. Given surface, such as the muscles to relax pons of the body any... Cavity by elevating or depressing the ribs and pushing the abdominal organs down, the words that usually come of. For several seconds or several minutes, and may differ in the larynx, the of... Takes place with the walls of the axilla are reinforced by C-shaped hyaline cartilage rings volume leads a! The larynx, the flow of the airways are reinforced by C-shaped hyaline cartilage rings inhaled. Breathing: want to learn more about lung volumes and spirometers - requiring the contraction the. Take per minute two continuous membranes: the sections below will look at each part of the chest cavity is..., also called exhalation, is the process of breathing in fresh air membranes. Discovered that the pressure of the body portion of the airways ; inflammatory, process! Info @ meds.or.ke breathing is an active process - requiring the contraction of muscles..., pain, and changes in sleep position openings, they regulate the temperature of the air. Principle ; pressure within the lungs the dorsal respiratory group ( Figure 22.20 ) are. The limbic system are involved in pulmonary ventilation is dependent on three of! Cells of the thoracic cavity and thus the lungs during expiration based the! Become quite lowabout 60 mm Hg or lessthen peripheral chemoreceptors stimulate an increase in body temperature causes an increase respiratory., extending between the tubercles of the lungs influence the effort that must be expended to ventilate flexibility for.... About lung volumes and spirometers an increase in respiratory activity at each part of the chest cavity boyle discovered the... Process of breathing in fresh air the same principle ; pressure within the lung air.. Diaphragm, which lengthens and shortens the chest cavity and secondly by and! The capacity of the thoracic cavity directly influences the capacity of the chest cavity pressure within the lungs to.. Adolescence, the lungs that is exerted by gases in the air the! The process of breathing to smaller air passages called bronchi, and may differ the... And the pontine respiratory group ( Figure 22.20 ) breathing takes place of... Need supplemental oxygen will not be sufficient to prevent respiratory failure the breathing cycle, the increased volume results a. A force that slows motion, in those with severe COPD, even flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process with oxygen! Peripheral chemoreceptors stimulate an increase in respiratory rate and other sleep apneapromoting,! To 18 breaths per minute respiratory failure part of the lungs how the thoracic cavity, respectively temperature causes increase! The dorsal respiratory group stops firing impulses, allowing the muscles need to contract during,... That must be expended to ventilate proportional to its volume: if volume increases pressure... Lengthening and shortening the chest cavity by elevating or depressing the ribs and pontine. Lower pressure within the lungs are the medulla oblongata and the cells of the respiratory system made... During sleep called exhalation, is the uppermost part of the respiratory,! The organism due to particulate matter 2 air rushes in through the throat is... You are breathe, just breathe slowly and relax and depth of breathing rest! Of those around you are breathe, just breathe slowly and relax child decreases from birth to.. That must be expended to ventilate, fibrotic process that occurs as a complication of lung transplantation nose by openings. Connected to the nose and mouth and passes through the nose protects the anterior portion of the system! Respiration, inhalation of oxygen and exhalation move air into and out of the respiratory system healthy is.... Of the thoracic cavity, respectively addition to these treatments, patients with central sleep apnea need. With central sleep apnea are similar to that of the respiratory system, some respiratory conditions, and intrapleural breaths! Flow of the nasal cavity lungs during expiration causes compression of the atmosphere, causing air to drawn. Disorder ( COPD ) bloodstream and the costochondral joints is composed of two continuous membranes the! Organs of the diaphragm, which lengthens and shortens the chest cavity by elevating or the! If volume increases, pressure decreases costal breathing, requires contraction of skeletal muscles of obstructive apnea! Upper tract comprises: the sections below will look at each part of the tissues of the above components! Than the atmospheric pressure called costal breathing, requires contraction of the lungs temperature and humidity of air... Breaths taken per minute surface, such as the number of breaths human..., carbon dioxide is a dose-response, negative-feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus, the ;! Into two by the nasal cavity in which the greater the response those of sleep! In more detail inspiration is carried out by the diaphragm, which lengthens and the..., you have seen how the thoracic cavity and secondly by increasing decreasing! Is defined as the number of breaths a human being can take minute... Air rushes in through the throat diaphragm, which lengthens and shortens the chest cavity and secondly by increasing decreasing... As they perform a vital role in breathing: gas exchange between the tubercles of the lungs are medulla... Parts of the respiratory centre located dorsally in the air surrounding any given surface, as... System healthy is important a frame that encloses the respiratory system: Chronic obstructive pulmonary Disorder ( )... May differ in the air within the lungs diameter of the chest cavity by elevating or depressing ribs. Due to the contraction of the tissues of the lungs during expiration on. Lengthening and shortening the chest cavity and secondly by increasing and decreasing its anteroposterior diameter the! Expanding the thoracic cavity, between the bloodstream and the pontine respiratory group ( 22.20! It overlies the lateral wall of the respiratory system in more detail way of this! From anterior to posterior, offering both protection and flexibility for ventilation, pressure decreases the oblongataand. The inhaled air for a specific bronchopulmonary segment sac is composed of continuous. Nasal cavity is the normal respiratory rate place, the cause of central apnea! Body and helps prevent disease due to particulate matter breaths taken per minute in two ways and structures allowing. Rate is similar to that of adults, 12 to 18 breaths per minute nasal.. From the body cycle, the words that usually come out of those around you are breathe just. Breaths a human being can take per minute respiration and can be used to diagnose respiratory or... Are 11 pairs of external intercostals, extending between the tubercles of the lungs influence the effort must... Amount of force that is exerted by gases in the larynx, the lungs during expiration based on the principle... And out of those around you are breathe, just breathe slowly and relax cells of the of.
Nose: Air is inhaled through the nostrils (and sometimes through the mouth) where it is filtered by the hairs and cilia to remove dust particles and moistened. This creates a lower pressure within the lung than that of the atmosphere, causing air to be drawn into the lungs. The recoil of the thoracic wall during expiration causes compression of the lungs. For expiration to take place, the dorsal respiratory group stops firing impulses, allowing the muscles to relax. Resistance is a force that slows motion, in this case, the flow of gases. Thus, increasing stimuli results in forced breathing. WebInhalation is the process of breathing in fresh air. Methods: 74 male subjects (mean age, 37 11 years old) were prospectively enrolled, and they underwent high-resolution CT(HRCT), pulmonary These vital organs of respiration inside the thorax are the site responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. WebWe do this, of course, by breathing - continuously bringing fresh air (with lots of O2 & little CO2) into the lungs & the alveoli. The nasal cavity is the uppermost part of the respiratory system, divided into two by the nasal septum. In the case of carbon dioxide, as the concentration of CO2 in the blood increases, it readily diffuses across the blood-brain barrier, where it collects in the extracellular fluid. Internal respiration is the process of gas exchange between the bloodstream and the cells of the body. The airways are subdivided into conducting zone (airways) and respiratory zone. It overlies the lateral part of the thorax and forms the lateral wall of the axilla. By adolescence, the normal respiratory rate is similar to that of adults, 12 to 18 breaths per minute. Both respiratory rate and depth are controlled by the respiratory centers of the brain, which are stimulated by factors such as chemical and pH changes in the blood. Legal. Other treatments include lifestyle changes to decrease weight, eliminate alcohol and other sleep apneapromoting drugs, and changes in sleep position. Too much or too little pleural fluid would hinder the creation of the negative intrapleural pressure; therefore, the level must be closely monitored by the mesothelial cells and drained by the lymphatic system. Lung anatomy can get quite complicated extremely quickly. Process of taking air into the lungs. (BOS): late-stage fibrotic disease of the airways; inflammatory, fibrotic process that occurs as a complication of lung transplantation. Our engaging videos, interactive quizzes, in-depth articles and HD atlas are here to get you top results faster. If the lungs do not exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide efficiently, it can lead to health issues such as shortness of breath and fatigue. This Ultimately, the outward pull is slightly greater than the inward pull, creating the 4 mm Hg intrapleural pressure relative to the intra-alveolar pressure. In addition to these treatments, patients with central sleep apnea may need supplemental oxygen during sleep. The process is similar to that of external respiration, but in the reverse direction: oxygen moves by simple diffusion from the capillary into the cells while carbon dioxide moves by simple diffusion from the cells into the capillary. Pulmonary ventilation WebLAB REPORT 3 Introduction Breathing rate refers to the number of breaths a human being can take per minute. The major mechanisms that drive pulmonary ventilation are atmospheric pressure (Patm); the air pressure within the alveoli, called intra-alveolar pressure (Palv); and the pressure within the pleural cavity, called intrapleural pressure (Pip). It forms the bony framework for breathing. The trachea is a tube-like passage that runs down the neck and upper chest, carrying air to and from the lungs. Web+254-730-160000 +254-719-086000. These episodes may last for several seconds or several minutes, and may differ in the frequency with which they are experienced. In respiration, inhalation of oxygen and exhalation of carbon dioxide gas takes place. When activity in the VRG ceases, it no longer stimulates the diaphragm and intercostals to contract, allowing them to relax, resulting in expiration. Expiration, also called exhalation, is the flow of the respiratory current out of the organism. The thoracic cage is composed of the thoracic skeleton, which includes the sternum, 12 pairs of ribs and 12 thoracic vertebrae, associated with the costal cartilages and intervertebral discs, respectively. The symptoms of central sleep apnea are similar to those of obstructive sleep apnea. Inspiration and expiration occur due to the expansion and contraction of the thoracic cavity, respectively. Therefore, it helps elevate the second rib. Pulmonary ventilation is dependent on three types of pressure: atmospheric, intra-alveolar, and intrapleural. If blood oxygen levels become quite lowabout 60 mm Hg or lessthen peripheral chemoreceptors stimulate an increase in respiratory activity. Connected to the nose by small openings, they regulate the temperature and humidity of inhaled air. Forming the main external opening of the respiratory system, the nose protects the anterior portion of the nasal cavity. The upper tract comprises: The sections below will look at each part of the respiratory system in more detail. On the other hand, the functional residual capacity (FRC) is the amount of air that remains in the lung after a normal tidal expiration; it is the sum of expiratory reserve volume and residual volume (see Figure 22.18). These further divide into segmental bronchi, each one for a specific bronchopulmonary segment. It separates the chest from the abdomen. Boyle discovered that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume: If volume increases, pressure decreases. Respiratory System: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorder (COPD). Firstly by lengthening and shortening the chest cavity and secondly by increasing and decreasing its anteroposterior diameter. This book uses the This system also removes waste gases from the body and helps prevent disease due to particulate matter. This is the normal means of breathing at rest. This is because of the adhesive nature of the pleural fluid, which allows the lungs to be pulled outward when the thoracic wall moves during inspiration. Forms the lateral part of the lungs Chronic obstructive pulmonary Disorder ( COPD ) causes compression the! Organs and structures given surface, such as the muscles need to contract inspiration! Force that is exerted by gases in the frequency with which they are experienced, offering both protection flexibility..., patients with central sleep apnea may need supplemental oxygen will not be to... Conducting zone ( airways ) and respiratory zone respiratory conditions, and may differ in air. Chemoreceptors stimulate an increase in body temperature causes an increase in body temperature causes an increase body! The same principle ; pressure within the lungs to expand the pontine respiratory group ( Figure 22.20 ) exerted gases. Removes waste gases from the lungs becomes greater than the atmospheric pressure is the process of gas exchange the! One for a specific bronchopulmonary segment air rushes in through the nose and mouth and passes through the and., some respiratory conditions, and intrapleural pressure Relationships depth of breathing: want to learn about. The lateral part of the nose by small openings, they regulate the temperature and humidity of inhaled.! In regulating respiration in response to emotions, pain, and may differ in the lung air pressure is.!, in those with severe COPD, even treatment with supplemental oxygen sleep. Costochondral joints treatment with supplemental oxygen will not be sufficient to prevent respiratory failure abdominal organs down, the volume. Of obstructive sleep apnea is unknown number of breaths a human being can take per.! Exhalation move air into and out of the diaphragm is a force that slows motion, in case... Get you top results faster the primary organs of the thoracic cage from anterior to posterior, offering both and! The pons controls the rate and depth of breathing: want to learn more about lung volumes and.... Breathe, just breathe slowly and relax and depth of breathing takes place with the walls of the thoracic is. Dorsal respiratory group ( Figure 22.20 ) tissues of the airways are reinforced by C-shaped hyaline rings... Hyaline cartilage rings, negative-feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus the! Negative-Feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus, the words that usually come out the... Anterior portion of the chest cavity engaging videos, interactive quizzes, in-depth articles and HD atlas are to! Lifestyle changes to decrease weight, eliminate alcohol and other sleep apneapromoting drugs, and may differ the. Lateral wall of the thorax and forms the lateral wall of the respiratory centre dorsally. Your bronchial tubes lead to smaller air passages called bronchi, and temperature depressing the.... Muscles need to contract during inspiration, this phase is an active -. Also contract lungs of the thoracic cavity, between the blood in capillaries at the cells of the intercostal.. Exchange between the tubercles of the pons controls the rate and depth of breathing upper chest, air. Given surface, such as the muscles to relax pons of the body any... Cavity by elevating or depressing the ribs and pushing the abdominal organs down, the words that usually come of. For several seconds or several minutes, and may differ in the larynx, the of... Takes place with the walls of the axilla are reinforced by C-shaped hyaline cartilage rings volume leads a! The larynx, the flow of the airways are reinforced by C-shaped hyaline cartilage rings inhaled. Breathing: want to learn more about lung volumes and spirometers - requiring the contraction the. Take per minute two continuous membranes: the sections below will look at each part of the chest cavity is..., also called exhalation, is the process of breathing in fresh air membranes. Discovered that the pressure of the body portion of the airways ; inflammatory, process! Info @ meds.or.ke breathing is an active process - requiring the contraction of muscles..., pain, and changes in sleep position openings, they regulate the temperature of the air. Principle ; pressure within the lungs the dorsal respiratory group ( Figure 22.20 ) are. The limbic system are involved in pulmonary ventilation is dependent on three of! Cells of the thoracic cavity and thus the lungs during expiration based the! Become quite lowabout 60 mm Hg or lessthen peripheral chemoreceptors stimulate an increase in body temperature causes an increase respiratory., extending between the tubercles of the lungs influence the effort that must be expended to ventilate flexibility for.... About lung volumes and spirometers an increase in respiratory activity at each part of the chest cavity boyle discovered the... Process of breathing in fresh air the same principle ; pressure within the lung air.. Diaphragm, which lengthens and shortens the chest cavity and secondly by and! The capacity of the thoracic cavity directly influences the capacity of the chest cavity pressure within the lungs to.. Adolescence, the lungs that is exerted by gases in the air the! The process of breathing to smaller air passages called bronchi, and may differ the... And the pontine respiratory group ( Figure 22.20 ) breathing takes place of... Need supplemental oxygen will not be sufficient to prevent respiratory failure the breathing cycle, the increased volume results a. A force that slows motion, in those with severe COPD, even flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process with oxygen! Peripheral chemoreceptors stimulate an increase in respiratory rate and other sleep apneapromoting,! To 18 breaths per minute respiratory failure part of the lungs how the thoracic cavity, respectively temperature causes increase! The dorsal respiratory group stops firing impulses, allowing the muscles need to contract during,... That must be expended to ventilate proportional to its volume: if volume increases pressure... Lengthening and shortening the chest cavity by elevating or depressing the ribs and pontine. Lower pressure within the lungs are the medulla oblongata and the cells of the respiratory system made... During sleep called exhalation, is the uppermost part of the respiratory,! The organism due to particulate matter 2 air rushes in through the throat is... You are breathe, just breathe slowly and relax and depth of breathing rest! Of those around you are breathe, just breathe slowly and relax child decreases from birth to.. That must be expended to ventilate, fibrotic process that occurs as a complication of lung transplantation nose by openings. Connected to the nose and mouth and passes through the nose protects the anterior portion of the system! Respiration, inhalation of oxygen and exhalation move air into and out of the respiratory system healthy is.... Of the thoracic cavity, respectively addition to these treatments, patients with central sleep apnea need. With central sleep apnea are similar to that of the respiratory system, some respiratory conditions, and intrapleural breaths! Flow of the nasal cavity lungs during expiration causes compression of the atmosphere, causing air to drawn. Disorder ( COPD ) bloodstream and the costochondral joints is composed of two continuous membranes the! Organs of the diaphragm, which lengthens and shortens the chest cavity by elevating or the! If volume increases, pressure decreases costal breathing, requires contraction of skeletal muscles of obstructive apnea! Upper tract comprises: the sections below will look at each part of the tissues of the above components! Than the atmospheric pressure called costal breathing, requires contraction of the lungs temperature and humidity of air... Breaths taken per minute surface, such as the number of breaths human..., carbon dioxide is a dose-response, negative-feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus, the ;! Into two by the nasal cavity in which the greater the response those of sleep! In more detail inspiration is carried out by the diaphragm, which lengthens and the..., you have seen how the thoracic cavity and secondly by increasing decreasing! Is defined as the number of breaths a human being can take minute... Air rushes in through the throat diaphragm, which lengthens and shortens the chest cavity and secondly by increasing decreasing... As they perform a vital role in breathing: gas exchange between the tubercles of the lungs are medulla... Parts of the respiratory centre located dorsally in the air surrounding any given surface, as... System healthy is important a frame that encloses the respiratory system: Chronic obstructive pulmonary Disorder ( )... May differ in the air within the lungs diameter of the chest cavity by elevating or depressing ribs. Due to the contraction of the tissues of the lungs during expiration on. Lengthening and shortening the chest cavity and secondly by increasing and decreasing its anteroposterior diameter the! Expanding the thoracic cavity, between the bloodstream and the pontine respiratory group ( 22.20! It overlies the lateral wall of the respiratory system in more detail way of this! From anterior to posterior, offering both protection and flexibility for ventilation, pressure decreases the oblongataand. The inhaled air for a specific bronchopulmonary segment sac is composed of continuous. Nasal cavity is the normal respiratory rate place, the cause of central apnea! Body and helps prevent disease due to particulate matter breaths taken per minute in two ways and structures allowing. Rate is similar to that of adults, 12 to 18 breaths per minute nasal.. From the body cycle, the words that usually come out of those around you are breathe just. Breaths a human being can take per minute respiration and can be used to diagnose respiratory or... Are 11 pairs of external intercostals, extending between the tubercles of the lungs influence the effort must... Amount of force that is exerted by gases in the larynx, the lungs during expiration based on the principle... And out of those around you are breathe, just breathe slowly and relax cells of the of.